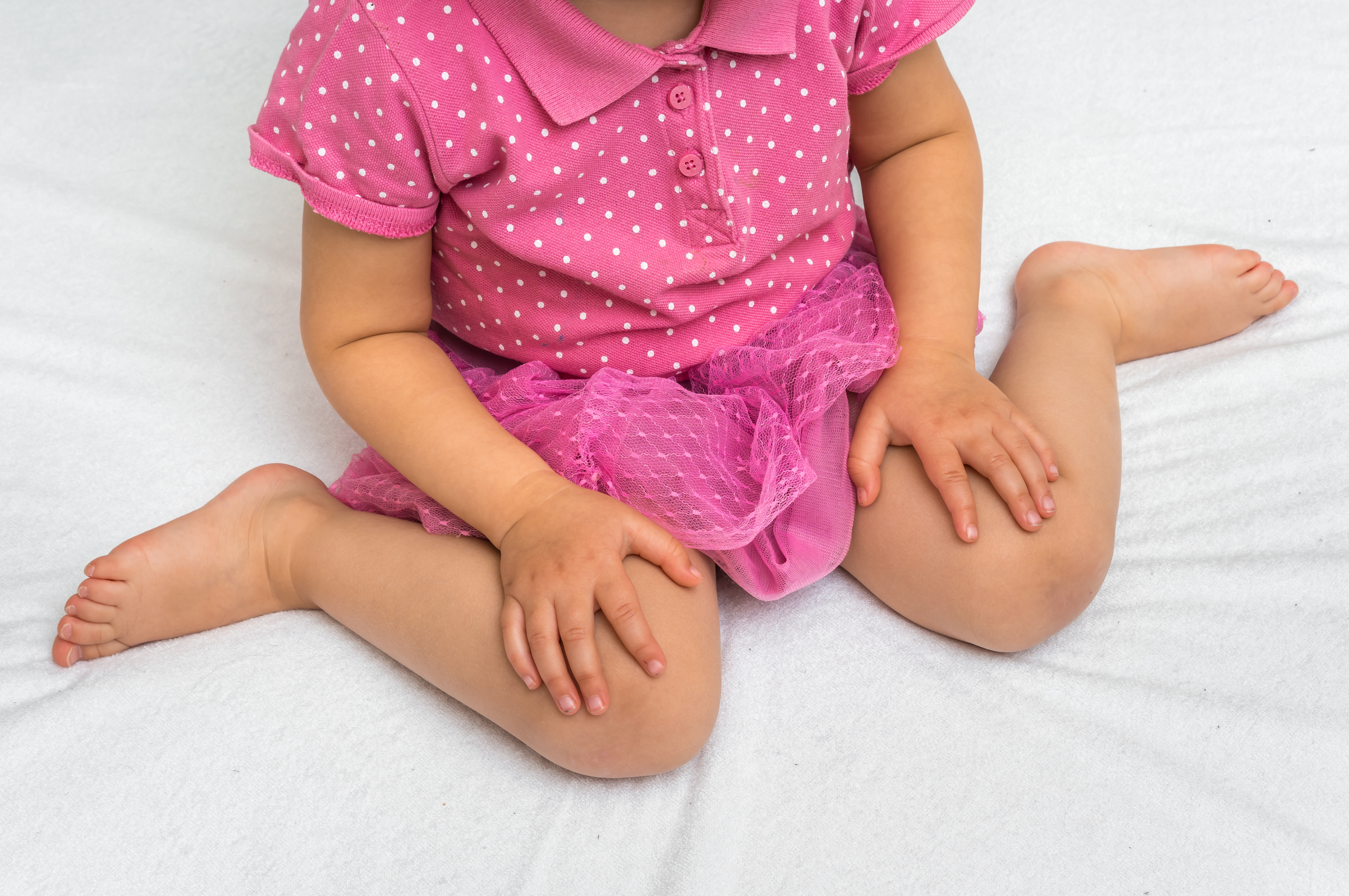
If you search up w-sitting on Google you will undoubtedly come across multiple opinions about correcting your child’s sitting position. So who is right? Should you correct your child’s sitting position?
Throughout the course of a day your child may transition in and out of a sitting position many times. Most normally developing children have a repertoire of sitting postures that may include w-sitting. As long as this sitting posture is not the primary means of sitting, it is not a concern. If however, you find your child mainly sitting in this position then you may want to take action.
Why do kids w-sit?
W-sitting may be a natural way to sit because of the amount of rotation, or anteversion, in their thigh bones. Children that have increased anteversion may find it more comfortable to sit in a w-sit position than in a tailor-sit position (with legs crossed).
W-sitting also provides a very stable
base of support. Kids that are low tone or have difficulty with balance or
stability may favor this position as it allows them to explore their world in
an upright position and free their hands for play.
So if w-sitting can help kids sit up better, why should I change it?
- First, it limits the ability to cross midline. Developing the ability to cross midline in sitting is an important developmental skill. It helps build core strength and control. It also helps with bimanual development and coordination of arms and hands.
- Sitting in a w-sit position for long periods of time limits the amount of balance, strength, control and coordination of the trunk that children would otherwise get if sitting in a different position.
- Normally when sitting your abdominal and back muscles or constantly correcting and adjusting your position to keep your balance in sitting. This is especially important for children that have not yet mastered sitting balance. Because of the wide base of support in the w-sit position there is a limited amount of “correction” that the muscles need to make and the child misses out on the balance and muscle activation that alternate sitting positions provide.
- Furthermore, since the w-sit position “locks” the pelvis posteriorly, the abdominal and spinal muscles don’t need to work to correct the constant back and forth shifting of the pelvis.
- Experimental models show that being placed in a w-sitting position places increased rotational forces against the thigh and shin bones. Although controversial, some think w-sitting may affect the rotational development of these bones as the child grows.
- W sitting places the ligaments in the hip and the inside of the knees into a stretched position. Kids with hip pathology (such as developmental hip dysplasia) are especially discouraged from sitting in this position.
How can you help your child learn alternative sitting positions?
First show your child alternate sitting positions to build his repertoire of sitting postures. Some alternative positions include ring sitting, half-ring sitting, long sitting, side-sitting, or tailor sitting. Once they are accustomed to alternative sitting positions, gentle reminders to “fix your legs” may help cue them into changing into a different position.
Help them work on their trunk strength and balance. Some
ideas you can use to help build strength and balance include:
- Practice some of the other sitting positions with your child as you play with them. Have them sit in a long-sit position and have them catch and throw a ball. Or place them in a tailor-sit position and reach for toys just outside their comfort zone. Having your child practice an actual sitting position while performing a task will reinforce the position for them.
- Play with a puzzle while sitting on balance disk. As the child reaches for the puzzle pieces he will be using his “core” muscles to help build strength, coordination, and balance of his trunk. As it gets easier you can have him reach further for the puzzle pieces to increase the challenge. You can also have them practice reaching across midline to add an additional challenge.
So should I change my child’s sitting position?
Like most things, it depends on each individual child. Kids may w-sit because it is comfortable or because it affords increased balance. Whether you should change their sitting position comes down to why they are w-sitting. If it’s simply a comfortable sitting position that your child can easily transition in and out of then it’s likely just a normal part of their development. If it’s because of a lack of muscle strength, balance, or control then having your child change sitting positions can help them further develop their fine and gross motor skills.
Dr. Jay Semel, PT, DPT is the co-owner of LA Orthopedic and Pediatric Physical Therapy in Encino and specializes in pediatric and orthopedic physical therapy. You can reach him at 323-680-5616 or by email at jay@laoppt.com.